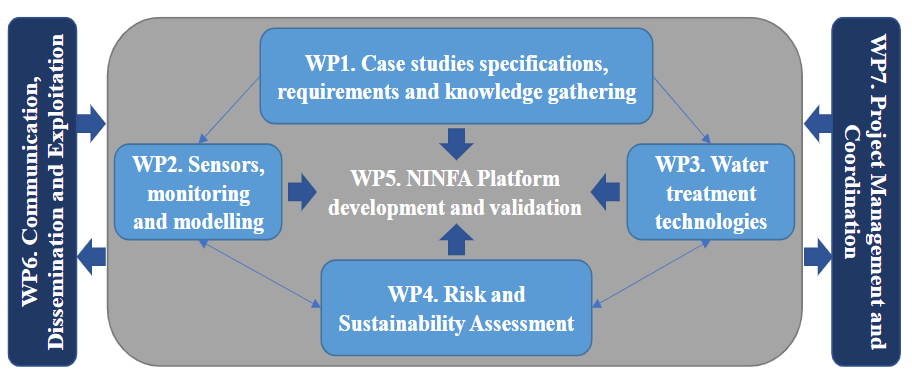
NINFA – TakiNg actIoN to prevent and mitigate pollution oF groundwAter bodies
Although several initiatives have developed actions and tools towards groundwater monitoring and protection, additional knowledge is needed to understand the synergistic effects and risks of multiple stressors and pollutants, and to develop cost-efficient groundwater monitoring strategies, pollution prevention/mitigation technologies, and early-warning DSS. NINFA will provide a novel strategy based on an early-warning DSS and knowledge database (NINFA Platform). Diffuse pollution affects 35% of the area of groundwater bodies with contaminants such as pesticides, herbicides, and nutrients (leading to eutrophication and lack of oxygen). Other pollution sources, including sewage from wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) and runoff infiltration in cities (especially during storm events), contaminate groundwater with contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) such as pharmaceuticals, microplastics and antibiotic resistance genes and with hydrocarbons and heavy metals, respectively. Moreover, aquifer exploitation for water consumption leads to increased pressure on groundwater resources, which may be aggravated by climate change (lack of aquifers' natural recharge). In coastal aquifers, this problem is worsened due to saline intrusion, mainly caused by water extraction, which affects the quality of the groundwater.
The innovative concept of NINFA is to facilitate the transition to a more effective decision-making system in groundwater management, by widening the knowledge on water flows, the in-situ mobility and transformation of CEC and establishing predictive models to promote the treatment and reuse of water and its quality.
Project website
Project coordinator
- Leitat
Project partners
-
Cetri
-
IMT
-
Wetsus
-
Wings
-
Deltares
-
Universita' di Roma
-
Aqualia
-
Hidrotec
-
Ayuntamient de los Alcazares